
Internet speed explained
So, you’ve taken a speed test to find out what speeds you’re getting in your home. But with tricky terminology and a handful of numbers, what does it all mean? Here, we’ll break it all down so that you can get a better understanding of what internet speed is and how it affects your online experience.

What is internet speed?
The term “speed” here is actually a little misleading. Internet speed tests actually compute the bandwidth allocated to your network, rather than how fast your internet runs. Bandwidth means the amount of data (in megabits) that can be sent in a certain about of time (in seconds). If your Internet bandwidth is 20 Mbps, for example, that would mean you can receive up to 20 megabits of data per second.
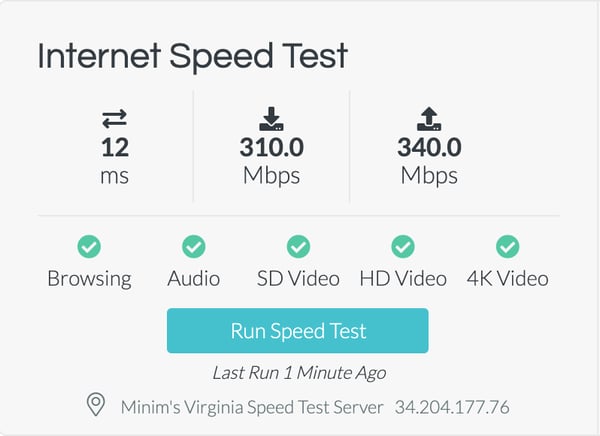
Image: A screenshot of Minim’s speed test service, measuring ping, download speed, and upload speeds. Minim’s speed test also shows the capabilities of a user’s internet speeds, such as streaming videos or browsing the web.
When interpreting the results of your internet speed test, there are several numbers that contribute to your overall internet experience. The most important of these is, arguably, your download speed, which is most likely the result a speed test will show you. Some speed tests will also show your upload speed and ping or latency, which typically only affects internet users who participate in online gaming or bandwidth-heavy streaming (think 4K-resolution movies).
Speed test terminology: what does it all mean?
When taking a speed test, the most typically seen measurement is the download speed of your home network. Download speeds measure the rate that data is transferred from the internet to your device (how long it takes your device to load websites or download files, for example). Correspondingly, upload speeds measure the rate that data is transferred from your device to the internet (uploading a photo to social media or sending a message online). Both download and upload speed are measured in megabits per second, or Mbps.
Ping, also referred to as latency, measures the reaction time of your connection—the amount of time it takes to send a request and receive a response, measured in milliseconds (ms). This is really only a statistic that factors into video conferencing or online gaming and will be noticeable in the form of lag. The best ping time you can have is zero.

Is my internet speed good?
There are many factors that can contribute to slow internet speeds, like the distance you are from your router or the number of users connected to your network. While understanding whether your internet speed is fast or slow is important, it’s just as important to know just what speeds you actually need. The typical household with four to five people needs about 200 Mbps to support a full range of bandwidth-hogging activities.
Below is a handy chart to gauge what speeds you may need:
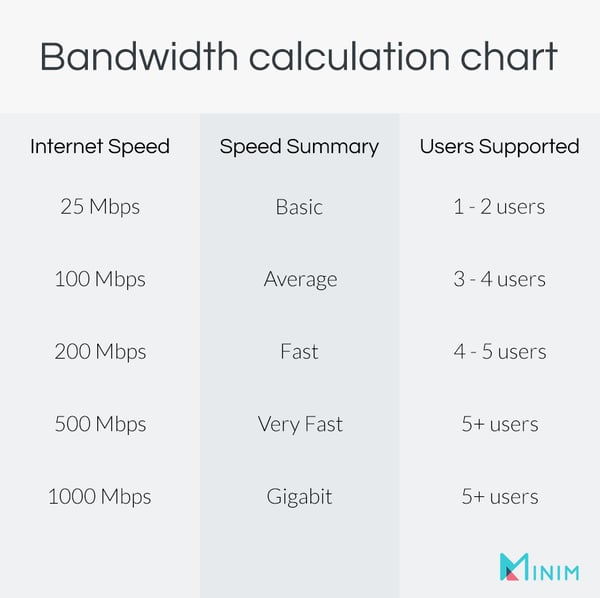
To better estimate what internet speed you actually need, take into account the types of activities you need to support. If you’re a gamer, for example, you may need a higher speed allocation than a casual web browser would.

If you’re still unsure of what speeds you need for your home, BroadbandNow has a handy calculator to calculate the minimum speeds you’ll need based on your internet activities.
Improving my WiFi speed without paying for a more expensive internet package
Are you paying for the perfect package but not getting the speeds you expected? Here are some tips for improving your internet experience:
- Move your router, modem, or router/modem combo to a centralized location in your home.
- Consider purchasing WiFi extenders or repeaters if you have a multi-level home. Don’t know the difference? Check out this blog.
- Switch over to the 5 GHz band on your WiFi network. The 5 GHz WiFi channel allows for faster speeds than the 2.4 GHz channel, although it doesn’t reach as far. Keep in mind that the distance from your router can affect your WiFi speed test results, as well as the device you’re on and connection type (wired versus wireless).
- Contact your ISP. There might be a number of reasons why you aren’t getting the speeds you expect, and your ISP can help troubleshoot them. If you're a Minim subscriber, you can use the Minim app to both measure and troubleshoot your WiFi.
More WiFi 101 topics you may like:
- WiFi boosters, repeaters, and extenders: What's the difference?
- How do I interpret my WiFi speed test results?
- Best WiFi analyzer apps for iOS and Android
- Understanding ping: How to reduce lag on your home network
- How do I test my WiFi speed at home?
- 3 steps to find the best WiFi channel for your router
- What are good download and upload speeds for home internet?
- What is WiFi 6?